The Scoping review: Bioinformatic analysis of the mecC gene in the Staphylococcus aureus strain
Palabras clave:
mecC gene, Staphylococcus aureus strain, MRSA, PRISMA Scoping-Reviews, geographic distributionResumen
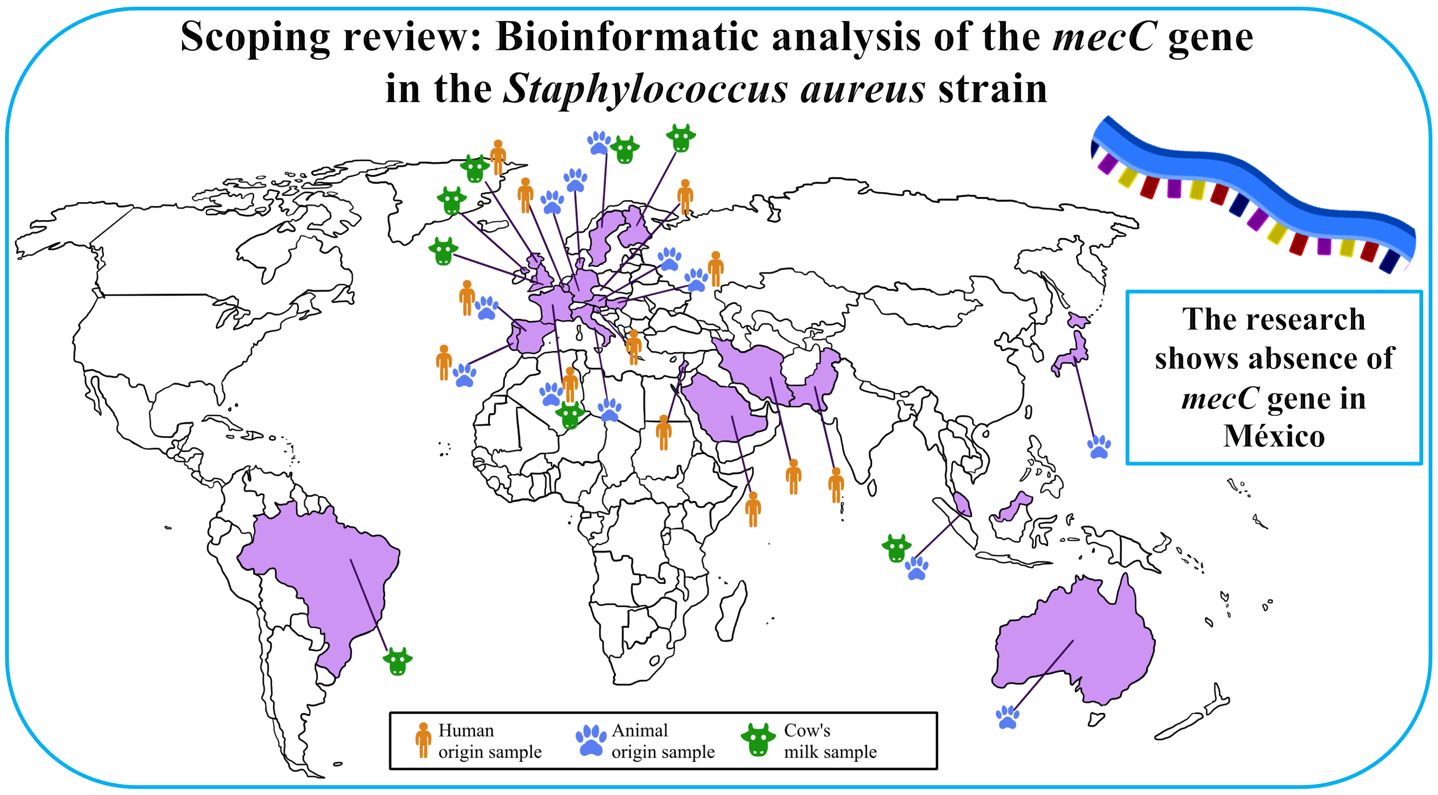
Antibiotic resistance is a natural phenomenon that has been accelerated due to its excessive use, resulting in longer hospital stays, increased patient mortality, and higher costs for treating infectious diseases. The Staphylococcus aureus strain is an opportunistic pathogen associated with nosocomial infections and often produces suppurative lesions; minor trauma and immunosuppression predispose to an infection development. The MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) strain has a SCCmec segment, it is constituted by a structural mec gene that codes the PBP2a protein. In 2011, García-Álvarez et al. made the first report of the mecC gene in MRSA strains, obtained from both bovines and humans; this gene shares 69% homology with the mecA gene, in addition to having zoonotic potential. A systematic review allows to analyze the geographical distribution of the gene and to understand the genomic characteristics of the studied strains. We employed the PRISMA extension for Scoping-Reviews; the information was collected from 2012 to 2023 in PubMed. The inclusion criteria were: 1) type of sample used in the study, 2) animal or human origin of the sample and 3) geographic region where the samples were taken. The presence of the mecC gene was observed in 25 countries around the world, with European countries accounting for the largest number of reports. The mecC gene was detected in MRSA strains in the SCCmec XI segment and most frequently with CC130 clonal complexes. During the development of the present investigation, no publications were found regarding the presence of this gene in México.
Archivos adicionales
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Categorías
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2025 Revista Ciencia Veterinaria y Biotecnología

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 4.0.




